Cloud Digital Leader

- 287 exam-style questions
- Detailed explanations and references
- Simulation and custom modes
- Custom exam settings to drill down into specific topics
- 180-day access period
- Pass or money back guarantee
What is in the package
CertVista practice exams are meticulously designed to replicate the actual Google Cloud Digital Leader certification experience. Every question follows the exact format, difficulty level, and scenario-based approach you'll encounter on exam day.
Use our practice exams as the final pit-stop to cross the winning line with absolute confidence and get AWS Certified! Trust our process; you are in good hands.
Complete domains coverage
CertVista comprehensively cover all six domains of the Google Cloud Digital Leader certification, ensuring you're prepared for every aspect of the real exam. Each domain is meticulously crafted to reflect the actual exam weightings and difficulty levels.
Digital Transformation with Google Cloud
Master the fundamentals of why cloud technology revolutionizes business, including cloud concepts, computing models, and shared responsibility. This domain covers organizations' strategic advantages when transitioning to Google Cloud, including improved scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. You'll learn to differentiate between cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid, and multicloud) and understand Google Cloud's core business transformation benefits: intelligence, freedom, collaboration, trust, and sustainability.
Exploring Data Transformation with Google Cloud
Dive deep into the value of data in digital transformation and how organizations unlock business insights through intelligent data management. This domain focuses on Google Cloud's comprehensive data management solutions, including BigQuery for analytics, Cloud Storage for object storage, Cloud SQL for relational databases, and Cloud Spanner for globally distributed databases. You'll master the concepts of data warehouses versus data lakes and learn how tools like Looker democratize data access across organizations.
Innovating with Google Cloud Artificial Intelligence
Explore AI and ML fundamentals and their practical business applications across industries. This domain covers the spectrum of Google Cloud's AI/ML solutions, from pre-trained APIs that require no machine learning expertise to custom model development using Vertex AI for maximum business differentiation. You'll understand when to use pre-trained APIs like Vision, Natural Language, and Speech-to-Text versus building custom models with AutoML or developing custom solutions.
Modernize Infrastructure and Applications with Google Cloud
Learn about comprehensive cloud modernization strategies, from simple lift-and-shift migrations to complete application reimagining. This domain covers the full spectrum of computing options available on Google Cloud, including virtual machines, containers, serverless computing, and managed services. You'll master the business value of containerization with Google Kubernetes Engine, serverless computing with Cloud Run and Cloud Functions, and understand how APIs create new business opportunities.
Trust and Security with Google Cloud
Master fundamental cloud security concepts and understand Google's defense-in-depth approach to infrastructure security. This domain covers today's top cybersecurity threats and how Google Cloud's security model addresses them through multiple layers of protection. You'll learn about encryption in transit and at rest, identity and access management, network security, DDoS protection, and compliance frameworks supporting data sovereignty requirements.
Scaling with Google Cloud Operations
Understand financial governance, cost management, and operational excellence at scale. This domain covers cloud financial governance best practices, resource hierarchy for access control, and tools for monitoring and controlling cloud consumption. You'll master concepts of modern operations, DevOps practices, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) principles, and how to design resilient, fault-tolerant systems while meeting sustainability goals.
Our questions mirror the real exam's scenario-based approach, testing your ability to apply Google Cloud knowledge to practical business situations rather than just memorizing facts. Each question presents realistic business challenges that require you to recommend appropriate Google Cloud solutions.
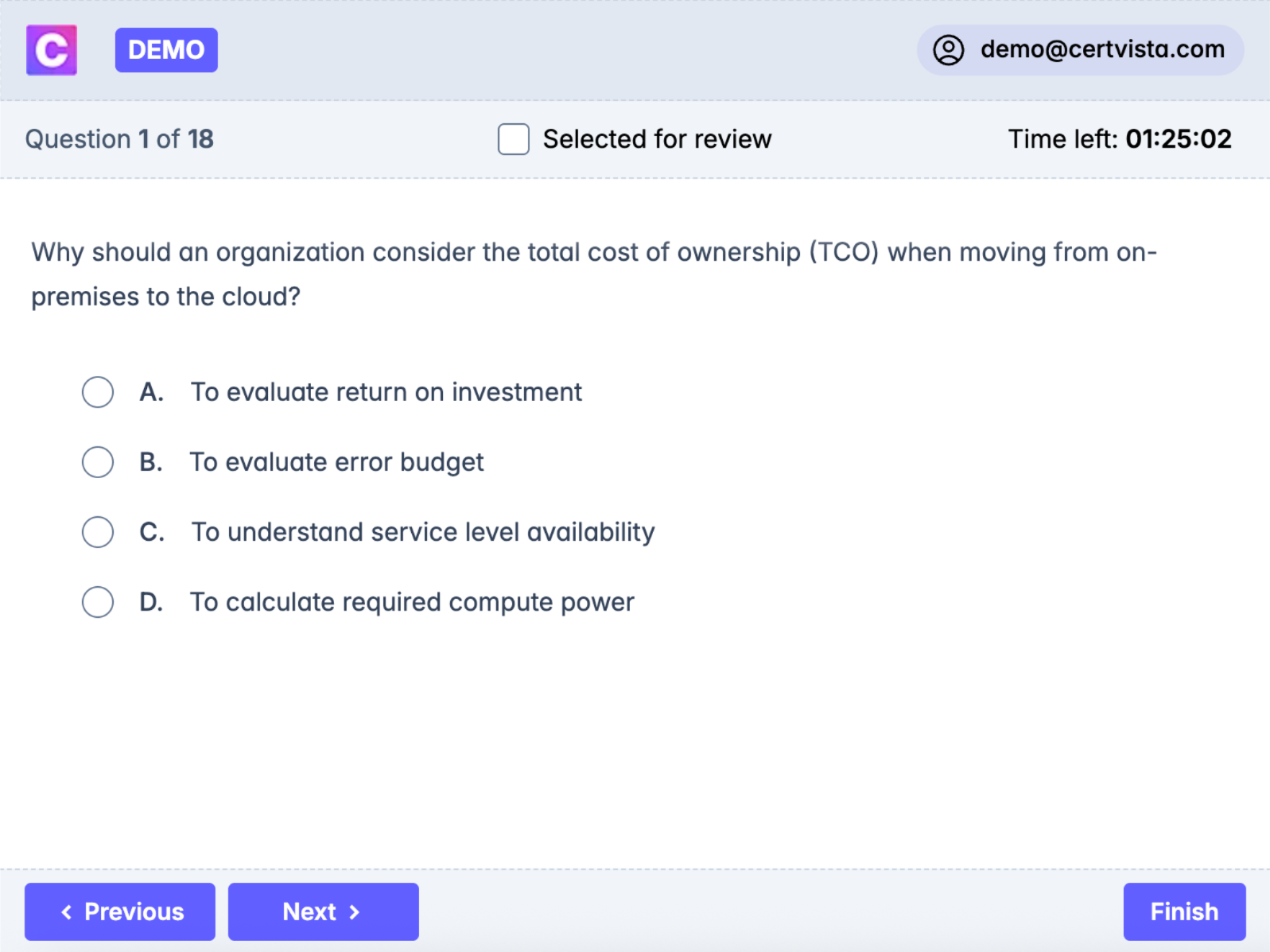
Experience the exact timing, interface, and pressure of the actual exam. Our simulation engine replicates every aspect of the testing environment to eliminate surprises on exam day. You'll practice with the same time constraints and question format you'll face during certification.
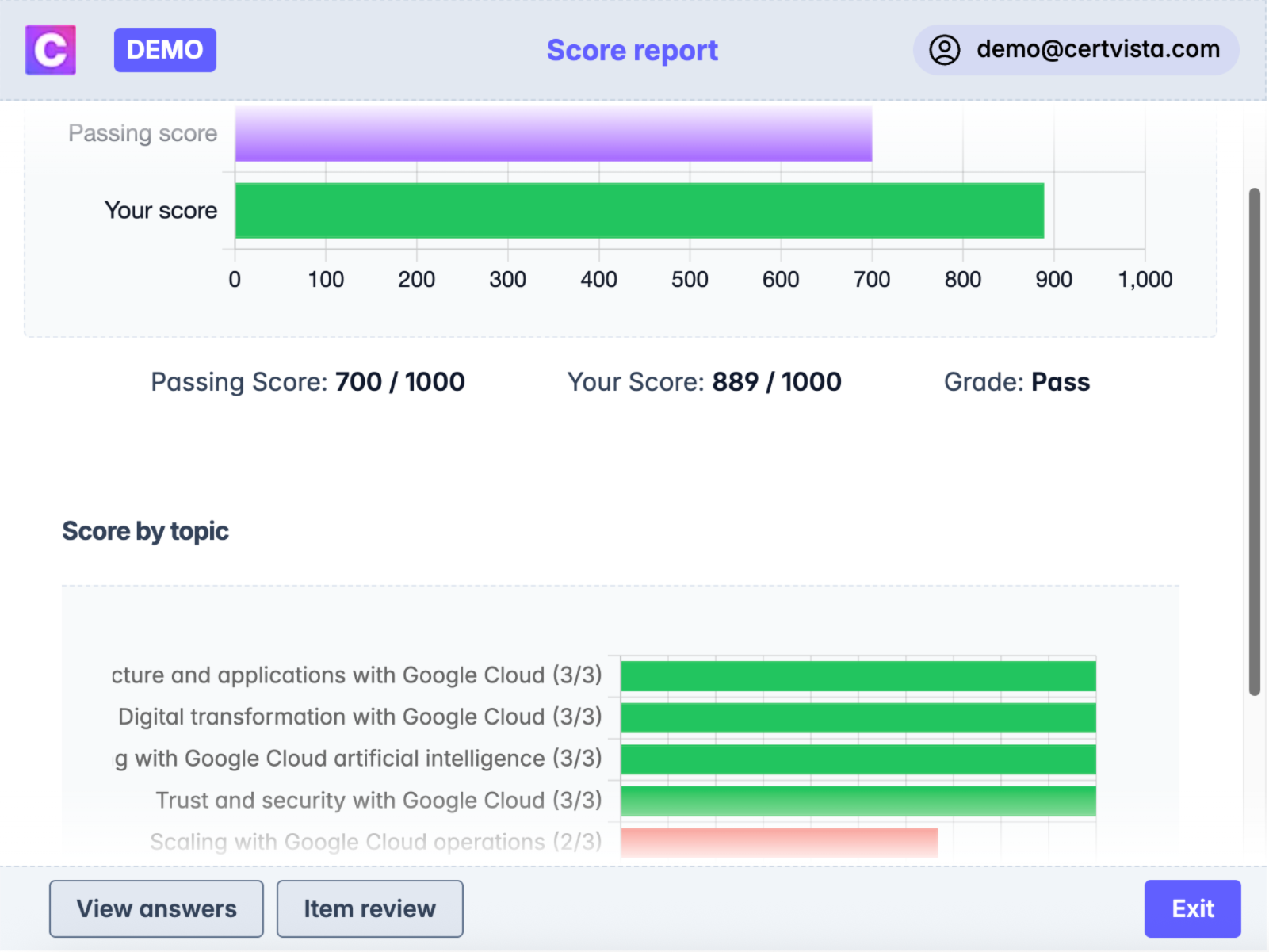
Get comprehensive insights into your performance across all domains. Our analytics identify knowledge gaps and track your improvement over time, with detailed explanations for every question that help you understand both correct and incorrect answers.
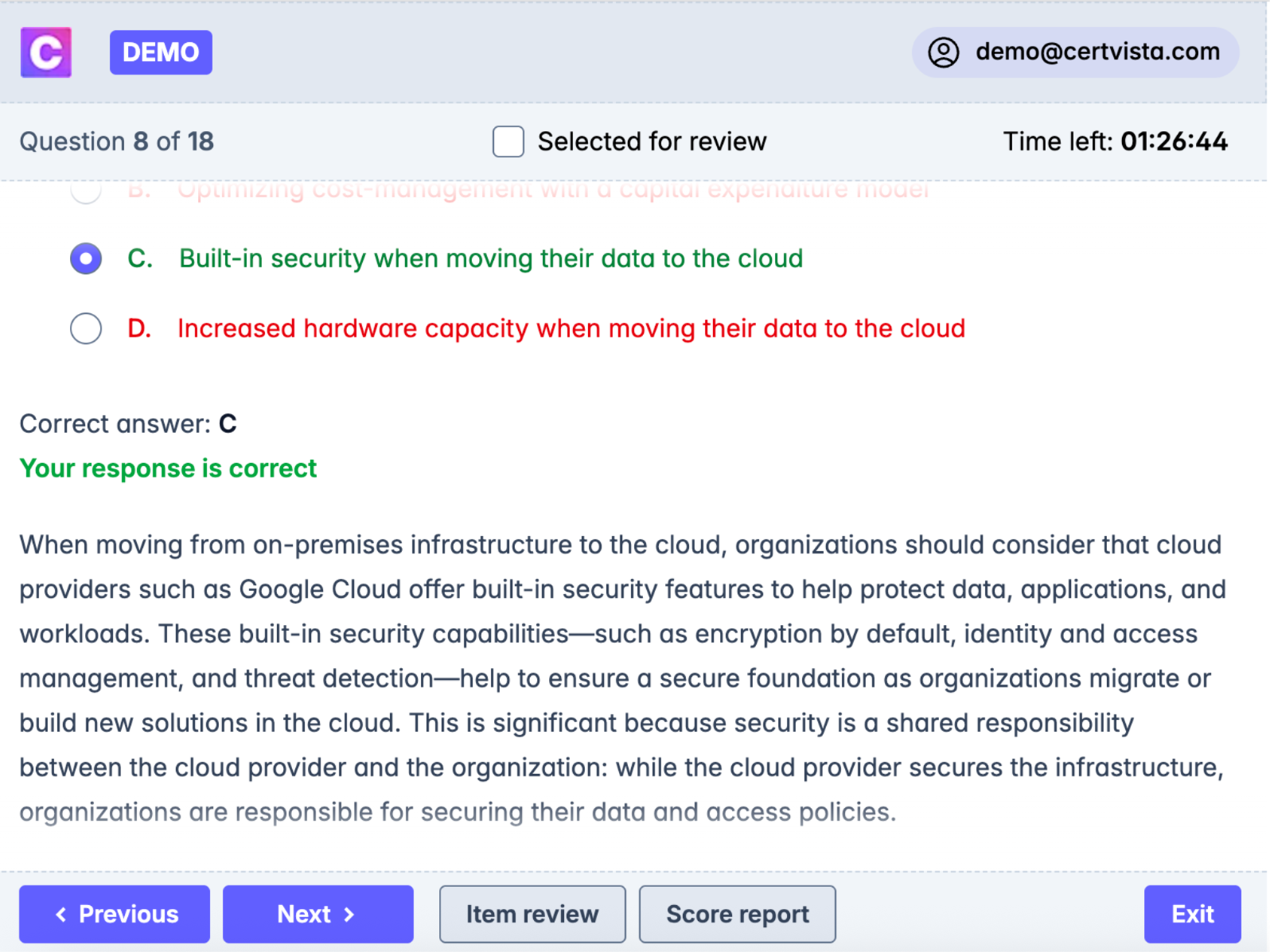
Every question includes detailed explanations written by Google Cloud professionals, helping you understand not just the correct answer, but the reasoning behind it. These explanations often include links to official Google Cloud documentation for deeper learning.
What's in the Cloud Digital Leader exam
The Google Cloud Digital Leader certification is designed for professionals who want to demonstrate their knowledge of cloud computing fundamentals and Google Cloud capabilities. Whether you're in sales, marketing, project management, or any role involving Google Cloud, this certification validates your expertise in articulating cloud value to organizations.
Exam Format and Structure
| Exam Detail | Specification |
|---|---|
| Number of Questions | 50 multiple-choice questions |
| Exam Duration | 90 minutes |
| Question Format | Multiple-choice with scenario-based questions |
| Passing Score | 70% (approximately 35 correct answers) |
| Available Languages | English and Japanese |
| Exam Delivery | Online proctored or at testing centers |
| Prerequisites | None (foundational level certification) |
| Certification Validity | 3 years from the certification date |
Question Types You'll Encounter
The exam focuses heavily on scenario-based questions that test your ability to recommend appropriate Google Cloud solutions for specific business challenges. You'll encounter questions about product selection, architectural decisions, cost optimization, security considerations, and migration strategies.
Business Scenario Questions Most questions present real-world business scenarios where you need to identify the most suitable Google Cloud services. For example, you might be asked to recommend the best data storage solution for a company with specific compliance requirements or suggest the most cost-effective compute option for a seasonal workload.
Architecture and Design Questions These questions test your understanding of how different Google Cloud services work together to solve complex business problems. You'll need to understand the trade-offs between different architectural approaches and recommend solutions that balance cost, performance, and scalability.
Cost Optimization Questions Expect questions about cloud financial management, including understanding different pricing models, recommending cost-effective solutions, and explaining how cloud adoption affects an organization's total cost of ownership.
Security and Compliance Questions These questions test your knowledge of Google Cloud's security model, compliance frameworks, and best practices for protecting data and applications in the cloud.
The exam emphasizes understanding the "why" behind recommendations, not just knowing what services exist. You'll need to demonstrate practical application of knowledge rather than rote memorization of product features.
Preparation Strategy
Focus on Business Value Unlike technical certifications that focus on implementation details, the Digital Leader exam emphasizes business value and strategic decision-making. Study how Google Cloud services solve business problems and create competitive advantages.
Understand Service Differentiation Know when to use each Google Cloud service and understand the key differentiators. For example, understand when to recommend Cloud SQL versus Cloud Spanner, or when serverless computing provides more value than traditional virtual machines.
Practice Scenario-Based Thinking The exam tests your ability to apply knowledge to realistic business situations. Practice analyzing business requirements and mapping them to appropriate Google Cloud solutions.
Sample questions
Get a taste of the Cloud Digital Leader exam with our carefully curated sample questions below. These questions mirror the actual exam's style, complexity, and subject matter, giving you a realistic preview of what to expect. Each question comes with comprehensive explanations, relevant documentation references, and valuable test-taking strategies from our expert instructors.
While these sample questions provide excellent study material, we encourage you to try our free demo for the complete exam preparation experience. The demo features our state-of-the-art test engine that simulates the real exam environment, helping you build confidence and familiarity with the exam format. You'll experience timed testing, question marking, and review capabilities – just like the actual certification exam.
An organization needs to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in its raw, native format in the same repository.
Which cloud data management solution should the organization use?
Data field
Database
Data lake
Data warehouse
A data lake is designed to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in its raw, native format. It provides a scalable and cost-effective way to centralize all types of data, supporting the ingestion and retention of massive data volumes from a variety of sources. Data stored in a data lake can later be processed, transformed, and analyzed as needed.
A database is generally tailored for structured data with predefined schemas and is less suitable for handling large volumes of unstructured or raw data. A data warehouse is optimized for analytical queries and typically stores structured, curated, and processed data, making it less ideal for raw, native formats. A data field refers to an individual piece of data within a database or table and is not a data management solution.
Look for keywords like raw, native format and all types of data (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) in exam questions—these typically indicate a data lake.
An organization wants its users to validate a series of new features for their app.
Why should they use App Engine?
Because their app is containerized and enabled by microservices.
To run different versions of the app for the same user.
Because the updated app will only include new features.
To run different versions of the app for different users.
App Engine supports traffic splitting, which allows organizations to deploy multiple versions of an application and direct different portions of traffic—or specific user requests—to these versions. This is especially valuable for running various versions of the app for different users, enabling A/B testing and quick feature validation in a production-like environment. This approach accelerates release cycles, helps gather user feedback on new features safely, and reduces risk before a full rollout.
Running different versions for the same user is not a typical use case enabled by App Engine's traffic management. The fact that the app is containerized and using microservices is aligned with Cloud Run or GKE, but does not uniquely leverage App Engine's strengths in version management and traffic splitting. Merely updating the app with new features does not require App Engine specifically; the unique benefit is controlled rollout and versioning.
Look for keywords like “run different versions for different users” or "traffic splitting" when questions focus on App Engine's advantages. Understand how App Engine enables experimentation and phased rollouts.
An organization delivers a proactive healthcare service. They want to efficiently and automatically collect patient data.
What should the organization encourage the patients to do?
Use at-home health screening devices and then upload their health data daily.
Self-assess their health data and then document and upload it in real time.
Visit a nurse who will use Internet of Things (IoT) devices to collect and upload their health data.
Wear Internet of Things (IoT) devices that upload their health data in real time.
In the context of proactively collecting healthcare data, leveraging wearable IoT devices offers the most efficient, automatic, and real-time approach. Wearable IoT devices, such as smartwatches or fitness trackers, continuously monitor metrics like heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. These devices are designed to securely upload data to healthcare databases or cloud services without requiring manual intervention from patients, thus increasing accuracy and timeliness.
Using at-home health screening devices and uploading data daily introduces significant manual steps, which can lead to data gaps, inconsistencies, or errors. Self-assessment and manual documentation further increase the risk of unreliable data and do not scale for continuous monitoring. Visiting a nurse using IoT devices may enhance data accuracy but is not efficient for ongoing, everyday monitoring as it relies on scheduled appointments and is resource intensive.
Focus on solutions that minimize manual effort, are scalable, and provide real-time data flow. The exam often highlights how cloud-connected IoT devices can transform industries—including healthcare—by enabling continuous and automatic data collection.
How would a global organization benefit from managing their data with Cloud Spanner?
Cloud Spanner is optimized to ingest unstructured data.
Cloud Spanner is optimized for cold storage.
Cloud Spanner visualizes and analyzes data in real time.
Cloud Spanner replicates data across regions in real time.
Cloud Spanner provides strong consistency and high availability by synchronously replicating data across multiple regions. For a global organization, this means their applications can access up-to-date data from anywhere in the world, and data is protected against regional failures. This real-time replication also improves reliability and supports global scale operations.
Cloud Spanner is not specifically designed for unstructured data—that is the domain of solutions like Cloud Storage or Firestore. It is a relational database, so it's optimized for structured data at scale.
It is also not for cold storage; cold storage solutions are typically more cost-effective for infrequently accessed data, such as Nearline or Coldline Storage, not a transactional database.
Cloud Spanner does not itself provide data visualization or real-time analytics features. While it supports real-time transaction processing, the analysis and visualization of data would be accomplished with products like BigQuery and Looker.
Pay attention to the description of the product—understanding whether a service is for structured versus unstructured data, or for hot versus cold storage, is often tested.
An employee receives an email from their internet service provider asking for their bank account number and password.
Which cybersecurity threat is this?
Distributed Denial of Service
Phishing
Ransomware
Spamming
This scenario describes an attempt to trick the employee into revealing sensitive information, such as a bank account number and password, by posing as a legitimate organization. This is a classic example of phishing, a social engineering attack in which attackers impersonate trusted entities to steal sensitive or confidential information. It does not involve overwhelming services (as in Distributed Denial of Service), encrypting files for ransom (as in ransomware), or simply sending unsolicited bulk messages (as in spamming). The main focus here is the deceptive effort to harvest credentials or financial data by exploiting human trust.
Look for key clues in scenarios: Requests for sensitive data, especially when posing as legitimate companies, almost always indicate phishing threats. Focus on the attack method's goal—stealing credentials versus overwhelming systems or sending bulk messages.
An organization wants to move from a tactical cloud adoption approach to a transformational approach.
How should they adapt the way they lead the organization?
Shift from an operational expenditure model to capital expenditure.
Invest in on-premises infrastructure to redesign relationships between IT and employees.
Drive cloud adoption with an individual contributor focus.
Increase top-down visibility and foster a culture of blamelessness.
Transformational cloud adoption is about more than simply migrating workloads or adopting new technology. It requires a cultural transformation and leadership capable of aligning the entire organization towards new ways of working. Increasing top-down visibility means leadership is engaged and transparent, supporting a clear vision and strategy for cloud adoption. Fostering a culture of blamelessness encourages innovation, experimentation, and learning from failure, which are all hallmarks of organizations that succeed with digital transformation using the cloud.
Moving to a capital expenditure model actually runs counter to cloud’s advantages, which emphasize operational expenditure (OpEx) through pay-as-you-go scaling. Investing in on-premises infrastructure is not aligned with a cloud-first, transformative approach—it suggests doubling down on legacy models. Driving cloud adoption through individual contributors without broader organizational leadership does not foster the systemic change needed for true transformation.
When faced with questions about cloud transformation, look for answers that mention leadership involvement, cultural change, and organization-wide strategies. Digital transformation isn't just technical—it's organizational.
Why is data stored in Google Cloud secure and private?
Data is encrypted by Cloud Data Loss Prevention.
Data is encrypted when an appropriate tag is applied.
Data is encrypted by default.
Data is encrypted by the Security Command Center.
Data stored in Google Cloud is encrypted by default. This means all customer content stored at rest is automatically encrypted, with no action required from the user. Google Cloud handles the key management and encryption processes for you, ensuring security and privacy of your data as part of its platform design. This approach meets a broad range of compliance and security needs.
Cloud Data Loss Prevention and Security Command Center are security tools that help you identify sensitive data and manage security across your cloud resources, but they do not perform default encryption of stored data. Encryption based on a specific tag also does not reflect Google Cloud's approach—encryption is automatic and does not rely on user-applied tags.
Look for phrases like "encrypted by default" in exam questions—they often indicate Google Cloud's security best practices for data at rest and in transit.
An organization wants to use multiple marketing datasets to forecast user acquisition.
How should they use cloud technology to gain new insights from the data?
Combine the datasets and make predictions using machine learning.
Separate the datasets and make predictions using machine learning.
Import the datasets into a custom data warehouse, and then archive old data.
Import and selectively archive the datasets in a custom data lake.
To gain new insights and forecast user acquisition, combining multiple datasets and utilizing machine learning is the recommended approach on Google Cloud. By aggregating marketing data, the organization can create a more comprehensive view, enabling machine learning models to detect patterns, trends, and make accurate predictions. This process maximizes the value of the data by leveraging advanced analytics and automated pattern recognition, which are key benefits of cloud-based AI services.
Separating datasets limits the context and reduces predictive accuracy. Simply archiving or selectively importing data does not leverage the predictive capabilities of cloud-based AI/ML solutions and may prevent real-time or in-depth analysis required for forecasting.
Focus on solutions that emphasize unifying data sources and utilizing AI/ML capabilities in the cloud. Look for key terms like "combine datasets" and "machine learning" when questions involve data-driven predictions.
Your organization stores highly sensitive data on-premises that cannot be sent over the public internet. The data must be processed both on-premises and in the cloud.
What should your organization do?
Configure Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) in your Google Cloud VPC network.
Order a Partner Interconnect connection with your network provider.
Create a Cloud VPN tunnel between Google Cloud and your data center.
Enable Private Google Access in your Google Cloud VPC network.
To securely connect on-premises environments to Google Cloud without sending sensitive data over the public internet, you need a dedicated, private connection. Partner Interconnect allows you to connect your on-premises network to your Google Cloud VPC via a supported service provider, ensuring that data does not traverse the public internet and meeting requirements for handling sensitive data. This enables secure, high-bandwidth, and low-latency connections suitable for processing data in both locations.
Configuring Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) helps manage access to applications, but does not provide a network-level connection or address private data transfers. Creating a Cloud VPN tunnel encrypts traffic over the public internet, but data still traverses shared infrastructure and might not satisfy regulatory or sensitivity requirements. Enabling Private Google Access allows resources in a VPC without external IPs to access Google services privately, but does not establish a link between on-premises environments and Google Cloud.
If a scenario emphasizes avoiding public internet use when moving sensitive data between on-premises and Google Cloud, Partner Interconnect or Dedicated Interconnect are the preferred solutions. Look for keywords like 'private connection,' 'no public internet,' and 'sensitive data.'
An organization wants to collect metrics and metadata from their cloud applications and put them into dashboards.
Which Google Cloud tool should they use?
Cloud Trace
Cloud Logging
Cloud Monitoring
Cloud Debugger
Cloud Monitoring is designed to collect metrics and metadata across Google Cloud and other cloud environments, and provides the ability to create dashboards for visualization. It enables organizations to monitor the health, availability, and performance of their applications by aggregating metrics in one place and representing them visually with customizable dashboards.
Cloud Trace is primarily focused on latency data and distributed tracing, not comprehensive metrics collection or dashboarding.
Cloud Logging specializes in collection and analysis of log data—not metrics or dashboarding per se.
Cloud Debugger is used for inspecting and debugging live applications in production, not for metric collection or dashboard visualization.
For questions about monitoring, metrics, or dashboard visualization, focus on Cloud Monitoring as the primary Google Cloud tool for these tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Google Cloud Digital Leader certification exam costs $99 USD, plus applicable taxes. Prices may vary by country or if purchased with a voucher.
The Cloud Digital Leader exam consists of multiple-choice and multiple-select questions. There are no hands-on labs or practical exercises in this exam.
The scheduled time for the Cloud Digital Leader exam is 90 minutes. This is the total time allotted to complete all questions.
The Cloud Digital Leader exam typically contains 50-60 questions. The exact number can vary slightly per exam instance.
The exam assesses understanding of: 1. General cloud knowledge and digital transformation. 2. Innovating with data and Google Cloud. 3. Infrastructure and application modernization. 4. Google Cloud security and operations. It focuses on capabilities, use cases, and benefits of Google Cloud products.
There are no official prerequisites for the Cloud Digital Leader exam. However, a foundational understanding of cloud computing concepts and familiarity with Google Cloud's core products and services is highly recommended.
Google Cloud does not publish the exact passing score for the Cloud Digital Leader exam. Exam results are provided as a simple pass or fail.
The Cloud Digital Leader exam is considered foundational or entry-level. It is designed for individuals in various roles who need to understand cloud capabilities and how Google Cloud can support business objectives, rather than deep technical implementation skills.
To prepare, review the official Google Cloud exam guide, utilize Google Cloud's recommended learning paths (e.g., on Cloud Skills Boost, CertVista), take official sample questions, and focus on understanding the business value and use cases of Google Cloud services.
Yes, Google Cloud provides official sample questions on the Cloud Digital Leader certification page. These help familiarize you with the exam question style and assess your readiness. In addition, CertVista's question sets provide hundreds of exam-style questions on a highly realistic test engine.
If you do not pass the exam, you must wait 14 days before attempting it again. If you fail a second time, you must wait 60 days. A third failed attempt requires a 365-day waiting period before retaking.
You can register for the Cloud Digital Leader exam through Webassessor, Google Cloud's official test delivery partner. You can choose an online proctored exam or take it at a designated testing center.
The Cloud Digital Leader exam is primarily offered in English and Japanese. Always check the official Google Cloud certification page for the most current list of available languages.
Using exam dumps (unauthorized collections of actual or supposed exam questions) violates Google Cloud's exam policies. It can invalidate your exam score, revoke your certifications, and ban you from future Google Cloud exams. You should focus on legitimate study materials.
The Cloud Digital Leader certification is valid for three years from the date you pass the exam. You must recertify before the expiration date to maintain your certification status.